Acetone or dimethyl ketone is a colorless, flammable solvent with a distinct, pungent odor. It’s used in the production of plastics, fibers, and other chemicals, as well as for cleaning and degreasing. It’s also found in nail polish remover.
| IUPAC Name | Propanone |
| Molecular Formula | C3H6O |
| CAS number | 67-64-1 |
| Synonyms | 2-Propanone, dimethyl ketone, dimethyl formaldehyde, pyroacetic acid, β-ketopropane |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C3H6O/c1-3(2)4/h3-4H,1-2H3 |
Acetone Properties
Acetone molar mass
The molar mass of acetone is 58.08 g/mol. This means that one mole of acetone contains 58.08 grams of the substance. The molar mass is an important physical property as it is used to calculate the number of moles of a substance in a sample and to determine the amount of a substance needed in a chemical reaction.
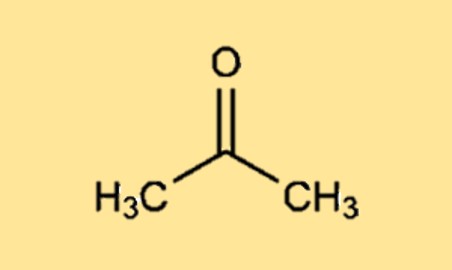
Acetone Structure
Dimethyl ketone (CH3C(=O)CH3) is a simple, three-carbon ketone with a molecular formula of C3H6O. The molecule has a carbonyl group (-C=O) at the center, with a methyl group (-CH3) on each side of the carbonyl group.
Acetone boiling point
The boiling point of acetone is 56.5°C. This means that at 56.5°C, the vapor pressure of dimethyl ketone is equal to the atmospheric pressure, causing the liquid to boil and convert into a gas. The boiling point is an important physical property as it is used to determine the purity of a substance and the conditions under which a substance can be distilled or evaporated.
Acetone melting point
The melting point of acetone is -94°C. This means that at -94°C, the solid dimethyl ketone will start to transition into a liquid. The melting point is an important physical property as it is used to determine the purity of a substance and the conditions under which a substance can be solidified.
Acetone density g/ml
The density of acetone is 0.7893 g/ml. This means that one milliliter of dimethyl ketone weighs 0.7893 grams. The density is an important physical property as it is used to determine the amount of a substance in a given volume.
Acetone molecular weight
The molecular weight of acetone is 58.08 g/mol. This means that one mole of dimethyl ketone molecules weighs 58.08 grams. The molecular weight is an important physical property as it is used to determine the number of moles of a substance in a sample and to calculate the amount of a substance needed in a chemical reaction.
| Appearance | Clear, colorless liquid |
| Specific Gravity | 0.79 |
| Color | Clear, colorless |
| Odor | Pungent, sweetish |
| Molar Mass | 58.08 g/mol |
| Density | 0.79 g/cm³ |
| Melting Point | -95.3°C |
| Boiling Point | 56.5°C |
| Flash Point | -20°C |
| Water Solubility | Miscible |
| Solubility | Soluble in most organic solvents |
| Vapour Pressure | 49.7 kPa at 20°C |
| Vapour Density | 2.05 g/L |
| pKa | 19.2 |
| PH | 3.0 (acidic) |
Acetone Safety and Hazards
Acetone is a highly flammable solvent with a strong odor. Prolonged exposure to acetone can cause skin irritation and respiratory problems. It is important to store dimethyl ketone in a well-ventilated area away from heat sources and sparks. When using dimethyl ketone, it is important to wear gloves and proper eye protection. Do not smoke or eat while using acetone, and avoid contact with open flames. If ingested, dimethyl ketone can cause digestive distress and should be immediately treated as a medical emergency. Proper handling and use of dimethyl ketone is crucial to ensure safety and prevent accidents.
| Hazard Symbols | Flammable |
| Safety Description | Dimethyl ketone is highly flammable and can easily ignite. |
| UN IDs | UN1090 |
| HS Code | 2914.11.00 |
| Hazard Class | 3 |
| Packing Group | II |
| Toxicity | Mildly toxic by inhalation, ingestion, and skin contact. |
Acetone Synthesis Methods
Acetone is synthesized using two main methods: the cumene process and the dehydrogenation process. The cumene process involves the alkylation of benzene with propylene to form cumene, which is then oxidized to form phenol and acetone. The dehydrogenation process involves the dehydrogenation of isopropyl alcohol, producing dimethyl ketone as a byproduct. Both methods are widely used in industry and result in high yields of dimethyl ketone. The cumene process is the most commonly used method for commercial dimethyl ketone production, as it is cost-effective and provides high purity dimethyl ketone. The dehydrogenation process is typically used for smaller scale production and for applications that require high purity dimethyl ketone.
Acetone Uses
People widely use dimethyl ketone as a solvent for various substances due to its colorless and volatile nature. In the cosmetic and beauty industry, it acts as an ingredient in nail polish removers, body lotions, and other skincare products. The manufacturing of pharmaceuticals, adhesives, and resins also requires acetone. It effectively cleans electronic components, degreases engines, and removes adhesive residues. Scientists use it as a solvent for various chemical reactions in the laboratory. Additionally, it improves engine performance as a fuel additive due to its low boiling point. Its easy evaporation without leaving any residue makes it an ideal choice for many applications.
