Sodium Bicarbonate (NaHCO3), also known as baking soda, is a white crystalline powder with a slight alkaline taste. It is commonly used as a leavening agent in baking, as a cleaning agent, and in the treatment of acid indigestion and heartburn.
| IUPAC Name | Sodium hydrogen carbonate |
| Molecular Formula | NaHCO3 |
| CAS Number | 144-55-8 |
| Synonyms | Baking soda, sodium acid carbonate, sodium hydrogen carbonate |
| InChI | InChI=1S/CHNaO3/c2-1(3)4/h(H,2,3)(H2,1,2,3)/p-1 |
Sodium Bicarbonate Properties
Sodium Bicarbonate molar mass
NaHCO3 molar mass is 84.007 g/mol. It is the sum of the atomic masses of its constituent elements – sodium, hydrogen, carbon, and oxygen.
Sodium Bicarbonate boiling point
Sodium hydrogen carbonate does not have a definite boiling point as it decomposes before boiling. The decomposition temperature of sodium bicarbonate is 851°C, at which point it decomposes into sodium carbonate, carbon dioxide, and water.
Sodium Bicarbonate melting point
Sodium hydrogen carbonate has a melting point of 50°C, at which point it changes from a solid to a white crystalline powder.
Sodium Bicarbonate density g/ml
The density of Sodium hydrogen carbonate is approximately 2.165 g/mL. This value can vary slightly depending on the particle size and degree of compaction of the material.
Sodium Bicarbonate molecular weight
The molecular weight of sodium bicarbonate is 84.007 g/mol, as calculated from its molecular formula NaHCO3.
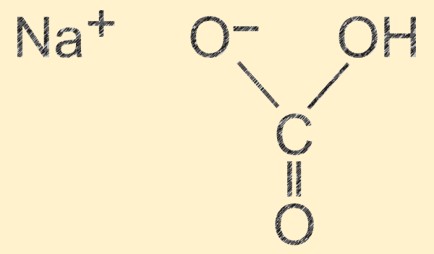
Sodium Bicarbonate Structure
Sodium hydrogen carbonate has a molecular structure that consists of one sodium ion (Na+), one hydrogen ion (H+), one carbonate ion (CO32-), and three oxygen ions (O2-). The ions are arranged in a repeating unit that forms a crystal structure, with hydrogen bonding between the molecules. The ionic nature of the compound gives it its basic properties, and the hydrogen bonding contributes to its physical stability.
| Appearance | White crystalline powder |
| Specific Gravity | 2.165 g/mL |
| Color | White |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Molar Mass | 84.007 g/mol |
| Density | 2.165 g/mL |
| Melting Point | 50°C |
| Boiling Point | Decomposes at 851°C |
| Flash Point | Not applicable |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in water |
| Solubility | Soluble in water |
| Vapor Pressure | Not applicable |
| Vapor Density | Not applicable |
| pKa | 8.1 |
| pH | 8.1 (10g/L, 25°C) |
Sodium Bicarbonate Safety and Hazards
Sodium bicarbonate is a safe and commonly used compound with a low level of toxicity. It is generally considered non-hazardous, non-flammable, and non-explosive. Ingestion of large amounts can cause digestive upset and may increase the risk of developing kidney stones. Skin contact may cause mild irritation, and inhalation of dust may cause respiratory irritation. It is important to handle NaHCO3 with care to avoid inhalation of dust and to avoid skin contact.
| Hazard Symbols | Not applicable |
| Safety Description | S24/25 |
| UN IDs | UN3077, ENVIRONMENTALLY HAZARDOUS SUBSTANCE, SOLID, N.O.S. (Sodium bicarbonate) |
| HS Code | 2836.90.90 |
| Hazard Class | 9 |
| Packing Group | III |
| Toxicity | Low toxicity when ingested, inhaled, or in contact with skin |
Sodium Bicarbonate’s Synthesis Methods
Sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) can be synthesized through several methods, including the Solvay process, which is the most commonly used method for large-scale production. The Solvay process involves the reaction of sodium chloride, ammonia, and carbon dioxide to produce sodium hydrogen carbonate and calcium chloride. Sodium hydrogen carbonate can also be synthesized through the reaction of NaHCO3 and carbon dioxide, or through the reaction of sodium hydroxide and carbon dioxide. These methods produce a high-purity form of NaHCO3, which can be further purified through recrystallization.
Sodium Bicarbonate’s Uses
Sodium hydrogen carbonate, commonly known as baking soda, has a wide range of uses due to its unique properties. In cooking, it is often used as a leavening agent for baked goods, such as cakes and breads. In personal care, it is used as a mild abrasive in toothpaste and as a deodorant. It is also used in the food industry as a pH adjuster and a neutralizing agent. Sodium hydrogen carbonate has medicinal uses as well, such as a treatment for heartburn, indigestion, and acidity. In addition, it is used in the production of cleaning products and fire extinguishers due to its fire-extinguishing properties. Sodium hydrogen carbonate also has environmental uses, as it can be used to neutralize acidic wastewater.
